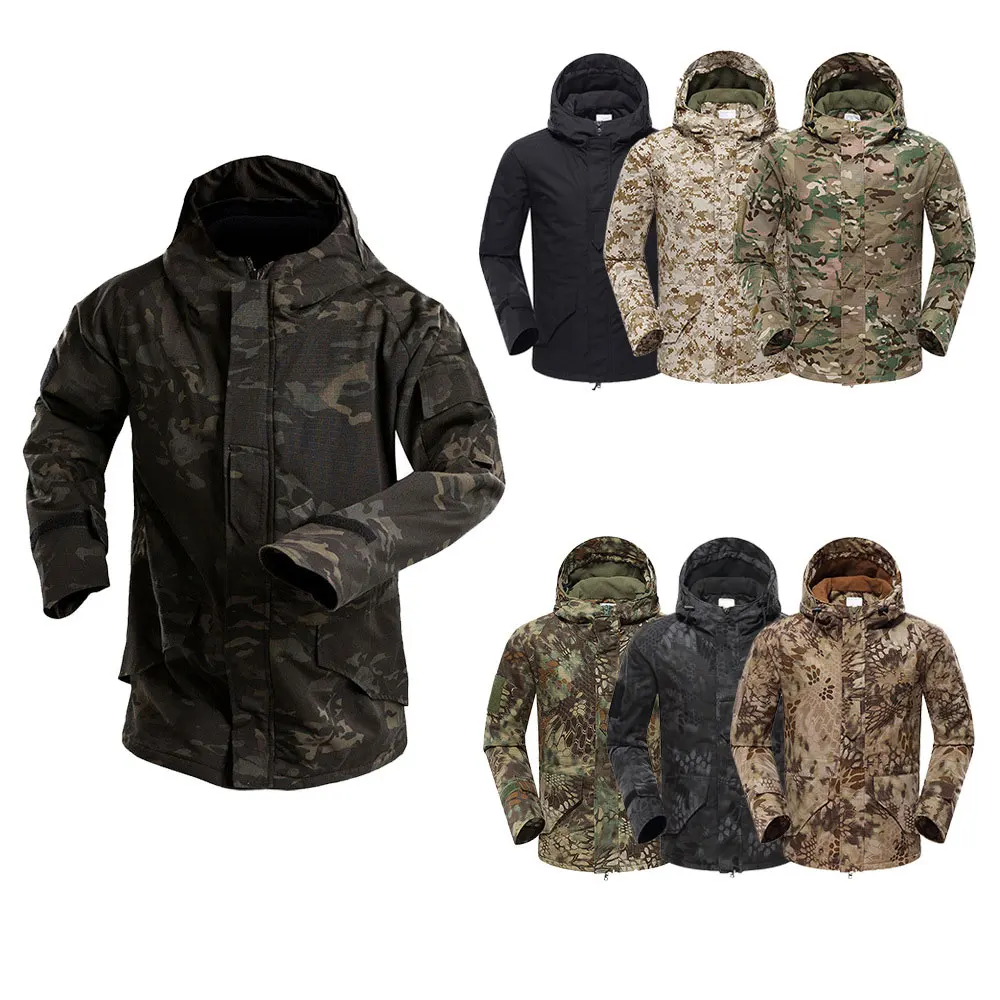
Tactical Gear
PRODUCTS
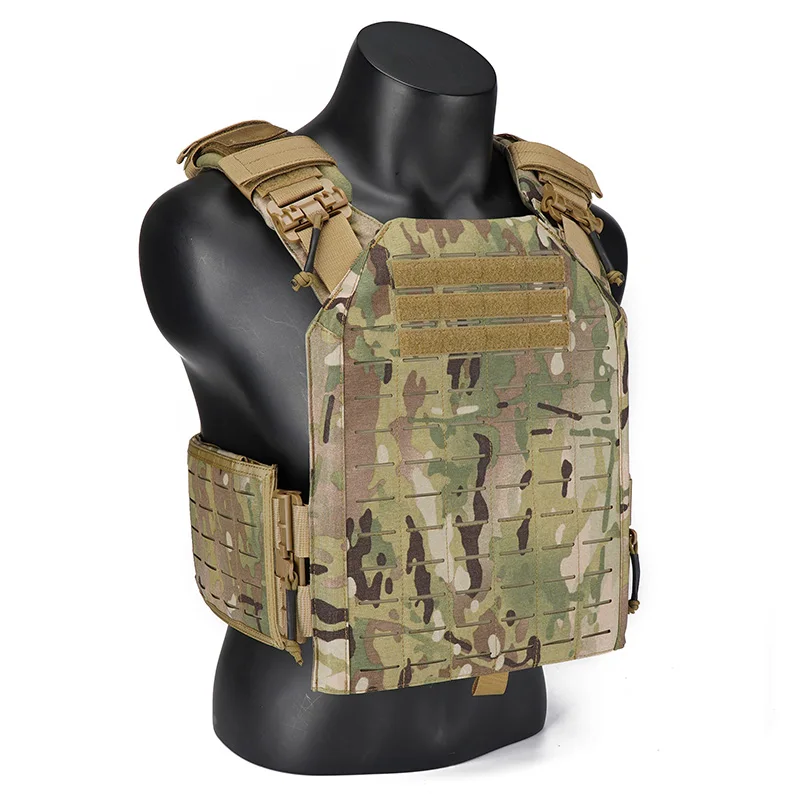
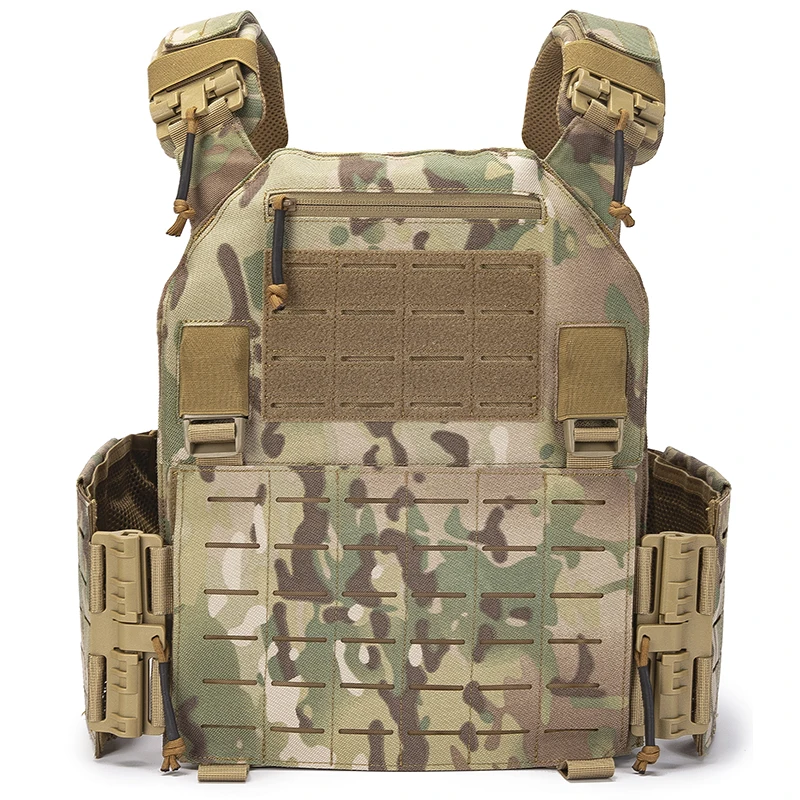
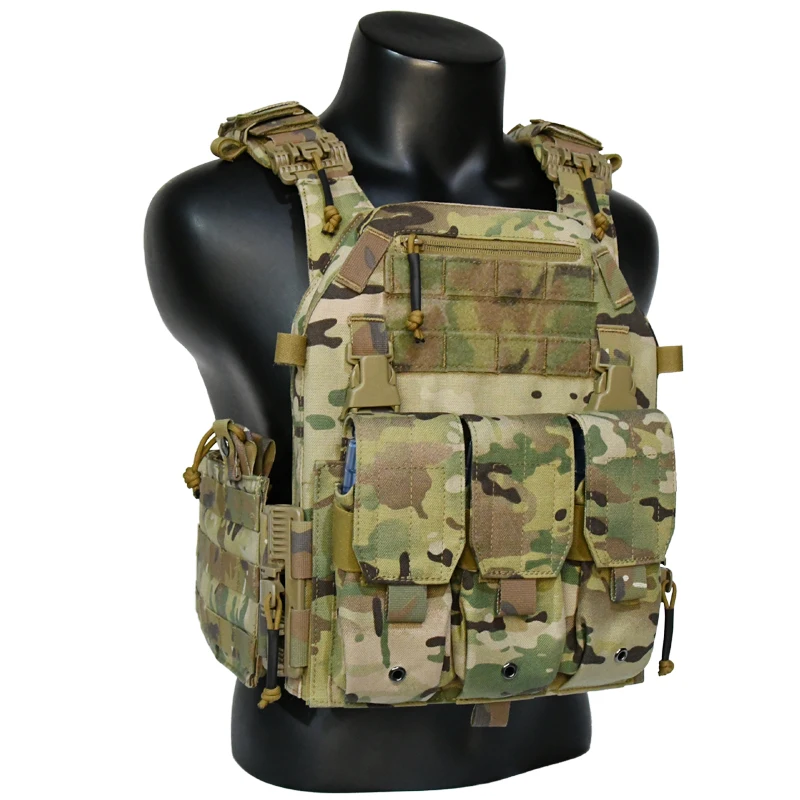
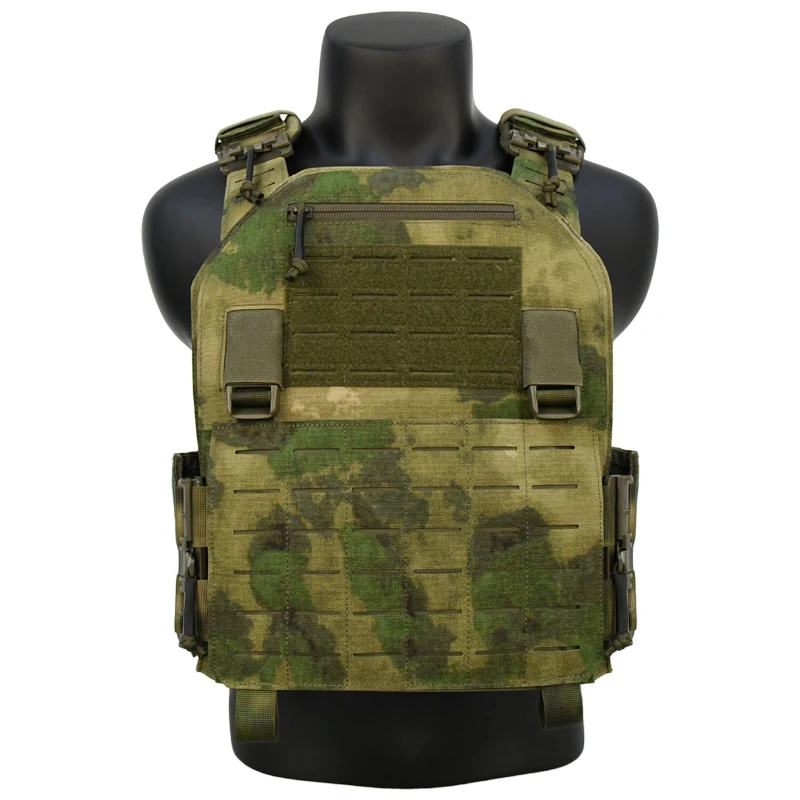
Understanding Tactical Vest Plates
Types of Tactical Vest Plates
Tactical vest plates are broadly categorized into several types, each offering different levels of protection and weight. Hard armor plates, typically made from ceramic or steel, provide the highest level of protection against rifle rounds. These plates are generally heavier and less flexible than other options. Steel plates, while offering excellent protection, can be quite heavy and are prone to fragmentation upon impact, posing a secondary threat to the wearer. Ceramic plates, on the other hand, are lighter and less prone to fragmentation, making them a popular choice despite a slightly higher initial cost.
Soft armor plates, often made from advanced polymers like polyethylene or aramid fibers, offer protection against handgun rounds and fragments. They are significantly lighter and more flexible than hard armor plates but provide less protection against high-powered rifle rounds. Many users opt for a combination of hard and soft armor plates, utilizing hard plates for primary ballistic protection and soft armor for additional coverage and comfort.
Finally, there are specialized plates designed for specific threats, such as those offering protection against stab wounds or blunt force trauma. These are often incorporated into more comprehensive body armor systems. The specific type chosen depends heavily on the anticipated threats and the user’s operational environment.
Plate Materials and Ballistic Ratings
The materials used in tactical vest plates directly impact their effectiveness and weight. Ceramic plates, often made from boron carbide or silicon carbide, offer high hardness and impact resistance, making them effective against high-velocity rounds. However, they can be brittle and prone to cracking under significant stress. Steel plates, usually made from hardened steel alloys, provide reliable protection but are significantly heavier than ceramic alternatives. Their weight can impact maneuverability and cause fatigue over extended periods.
Polyethylene plates, a popular choice for lightweight protection, offer a good balance between weight and protection. They are flexible and less prone to cracking than ceramic plates. Aramid fiber plates, similar to those used in bulletproof vests, offer protection against handgun rounds and fragments but are less effective against rifle rounds. The ballistic rating, usually expressed as NIJ (National Institute of Justice) standards, indicates the level of protection a plate offers against specific calibers and threats.
Understanding these materials and ratings is crucial for selecting the appropriate plate for a given situation. A law enforcement officer working in an urban environment might have different needs than a soldier operating in a combat zone.
Plate Fit, Weight, and Comfort
The fit of the tactical vest plates is as critical as their ballistic capabilities. Poorly fitting plates can restrict movement, compromise protection, and cause discomfort. Plates should be snug but not constricting, allowing for a full range of motion. The size and shape of the plates should match the dimensions of the vest carrier to ensure proper alignment and coverage.
Weight is another major consideration. Heavier plates provide greater protection but can lead to fatigue and reduced mobility. The overall weight of the armor system should be carefully considered in relation to the user's physical condition and the demands of their job. The addition of comfort features, such as breathable materials and adjustable straps, can greatly improve the wearability and functionality of the armor system.
Ultimately, the selection of tactical vest plates requires a careful balancing act between protection, weight, comfort, and cost. A thorough understanding of these factors, combined with a realistic assessment of the potential threats, is essential for choosing the right plates for the job.
SUBSCRIBE
INQUIRY